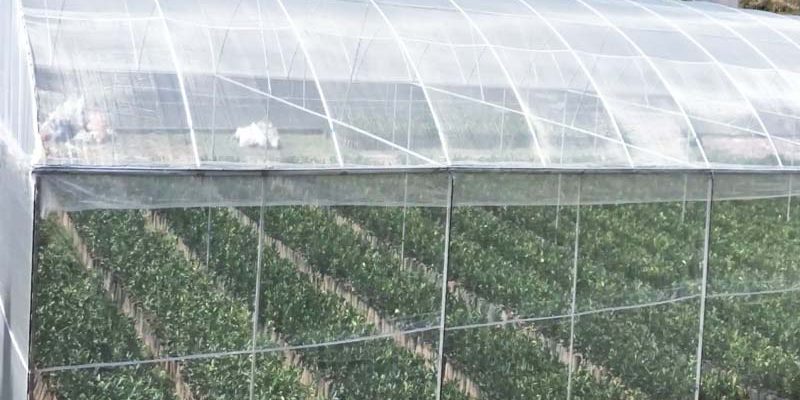
Excessive use of chemical pesticides has led to environmental pollution and raised concerns about food safety. As the demand for sustainable farming practices grows, insect nets have emerged as an effective alternative, helping farmers minimize pesticide application while shielding crops from pests. This article examines the working principles of insect nets, their impact on various crops, and offers practical advice for farmers to effectively utilize this eco-friendly tool in promoting sustainable agriculture.
How Agricultural Insect Nets Work
Agricultural insect nets serve as a physical barrier with mesh fine enough to block pests from reaching crops. Compared to domestic insect nets, those designed for agriculture are more resistant to UV rays, oxidation, and corrosion. They are typically made from high-quality polyethylene, enhanced with anti-aging and UV-resistant agents. This woven material is durable, heat-resistant, waterproof, corrosion-resistant, and non-toxic, making it well-suited for outdoor agricultural environments.
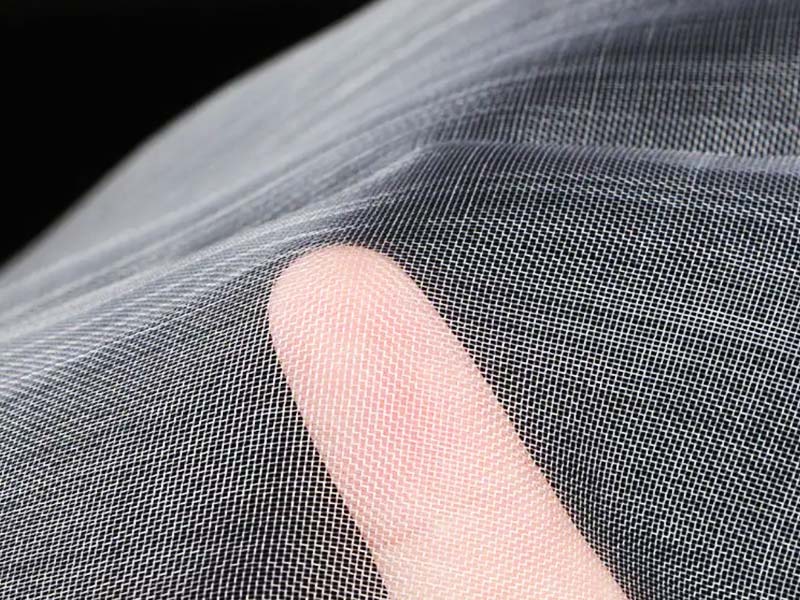

INSONSHADE insect net fabric
When placed over greenhouse vents or installed around crops, insect nets prevent common pests, including cabbage worms, aphids, and whiteflies. Our tests reveal that greenhouses using 50-mesh insect nets can reduce pesticide use by 50-80%, significantly cutting costs and providing farmers with long-term economic benefits.
Mesh Size and Aperture of Insect Nets
Insect net density is measured in “mesh,” which denotes the number of holes per square inch. Higher mesh counts indicate smaller holes, offering better protection against tiny pests. Standard agricultural insect nets range from 40 to 60 mesh, ideal for controlling small pests like aphids and whiteflies. When selecting the right net, consider both the mesh size and the aperture (or hole size), as these factors directly impact the effectiveness of pest control. Some brands may vary slightly in aperture size across the net’s length and width, which can affect overall performance.
Related Products: Greenhouse Anti-Insect Netting – Custom Mesh 20 to 100
Pest Size and Its Impact on Insect Net Effectiveness
The size of a pest, particularly its abdominal diameter, determines whether it can bypass an insect net. For instance, aphids have an abdominal diameter of 0.014-0.019 inches, while thrips are smaller, around 0.006-0.01 inches. When targeting more minor pests, selecting an insect net with an aperture matched to the pests’ dimensions can enhance control effectiveness.
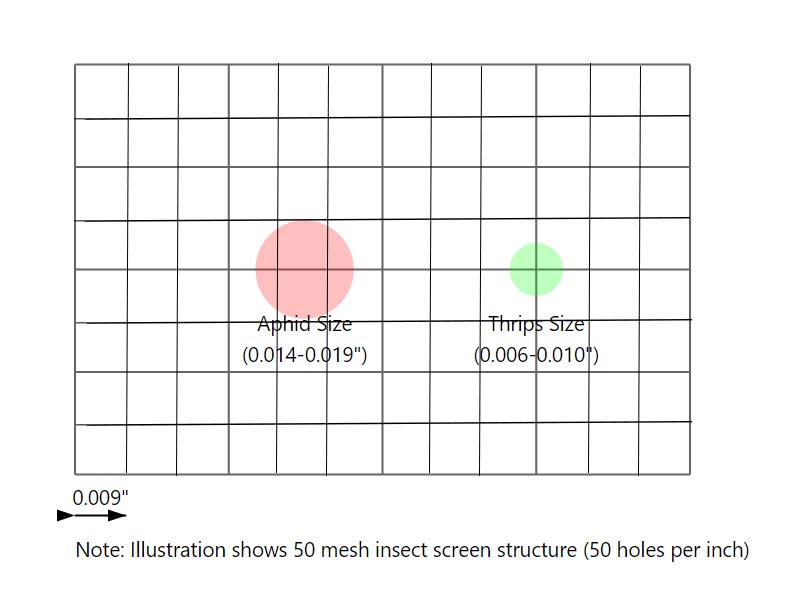
Pest Abdominal Diameter and Its Impact on Insect Net Effectiveness
Related Post: What Is Thrip Netting? How It Works
Pest species and sizes vary with location, climate, and crop type. For optimal results, analyze local pest populations before selecting a net and ensure it meets the specific crop protection needs.
Differences in Effectiveness Against Various Pests
The effectiveness of insect nets can vary depending on the size, flight capability, and color sensitivity of the pest.
- Different Pest Types: Insect nets help control many pests, including beet armyworms, diamondback moths, small cabbage loopers, and leafhoppers. They also shield crops from virus-spreading vectors, such as aphids, whiteflies, thrips, and American leafminers. For rice crops, insect nets offer exceptional control over rice planthoppers and rice leafrollers, achieving effectiveness rates of 99.4% and 100%, respectively.
- Mesh Size: The choice of mesh size affects performance against specific pests. Different mesh counts are most effective against specific pests, such as leafminers and thrips.
- Color Sensitivity: The color of insect nets can influence effectiveness. Thrips, for example, are highly attracted to blue, so using blue nets near greenhouses may inadvertently draw them closer. White nets prevent this issue. Red and black nets are less effective against spider mites, whereas white nets show the lowest pest infestation rates.
- Environmental Factors: Temperature and humidity levels impact the effectiveness of insect nets. While various insect net types remain durable under sunlight, their effectiveness against pests can vary with environmental changes.
Choosing the Right Insect Net Material
The most popular material for insect nets is high-density polyethylene (HDPE) with added UV stabilizers, providing a lifespan of 3-6 years. However, other materials with varying levels of durability and cost are also available:
- Polyethylene (PE): Made from woven PE fibers, these nets are durable and multifunctional. They protect crops from multiple pests and withstand wind and rain. They are widely used in vegetable production.
- Polypropylene (PP): Constructed from interwoven fibers, PP nets hold hole shape and size well. While they offer durability, PP is less resistant to weathering and longevity than PE.
- Nylon: Known for its high strength and wear resistance, nylon is used for areas needing high-strength protection, such as around livestock, to guard against significant pests and wildlife. However, nylon is generally less weather-resistant and durable than PE and PP, especially in extreme environments.
- Stainless Steel: Stainless steel and brass nets resist corrosion and rust, offering high durability and making them suitable for applications requiring robust, long-lasting protection. However, they are costlier, heavier, and require more complex installation and maintenance.
Finally
Insect nets with smaller apertures offer strong protection against pests, significantly reducing the need for pesticides and promoting a healthier crop environment. However, smaller apertures are not always ideal. While they improve pest control, they can also limit airflow, creating potential challenges. Reduced ventilation can lead to a less favorable growing environment, which negatively impacts crop health.
Additionally, a tighter mesh increases the risk of nets being damaged or blown away during strong winds or storms. Therefore, selecting the correct aperture size requires balancing effective pest prevention with adequate ventilation to maintain an optimal growing environment for crops. With careful selection and installation, insect nets can be a sustainable solution in promoting eco-friendly agricultural practices.
