Greenhouses are primarily designed to help plants survive winter. As summer approaches in the Northern Hemisphere, are the flowers, fruit trees, or vegetables in your greenhouse ready for the intense heat? The hot season presents significant challenges for their growth. Choosing the right shading materials not only blocks excessive sunlight but also provides a comfortable growth temperature for your plants. Therefore, selecting suitable shading materials is crucial for greenhouse farming in hot climates.
In this article, we will focus on the factors to consider when selecting shading materials for greenhouses and then share some best materials for greenhouses in hot climates, along with their characteristics and suitable scenarios.
Key Features of Best Greenhouse Shading Materials
When choosing greenhouse shading materials in hot climates, four key factors are crucial. Understanding these factors is vital for selecting the right type of shading material.
1. Shading Effectiveness
Since the goal is to shade your greenhouse crops, it’s essential to choose materials with excellent shading effectiveness. Such materials can effectively block excessive sunlight, preventing your greenhouse crops from sunburn and providing a comfortable growing environment.
Don’t Miss: What Percentage of Shade Cloth is Best for Greenhouse Plants?
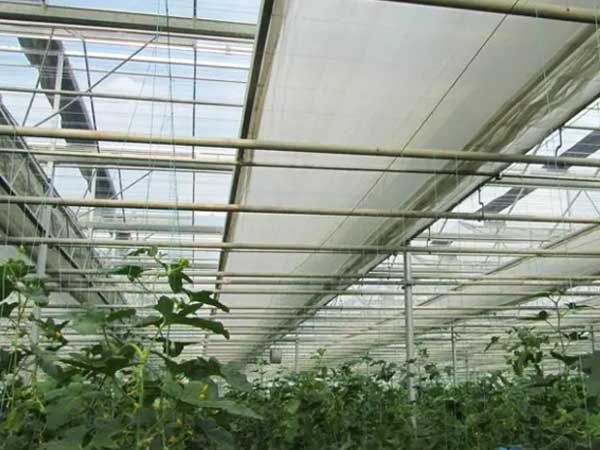

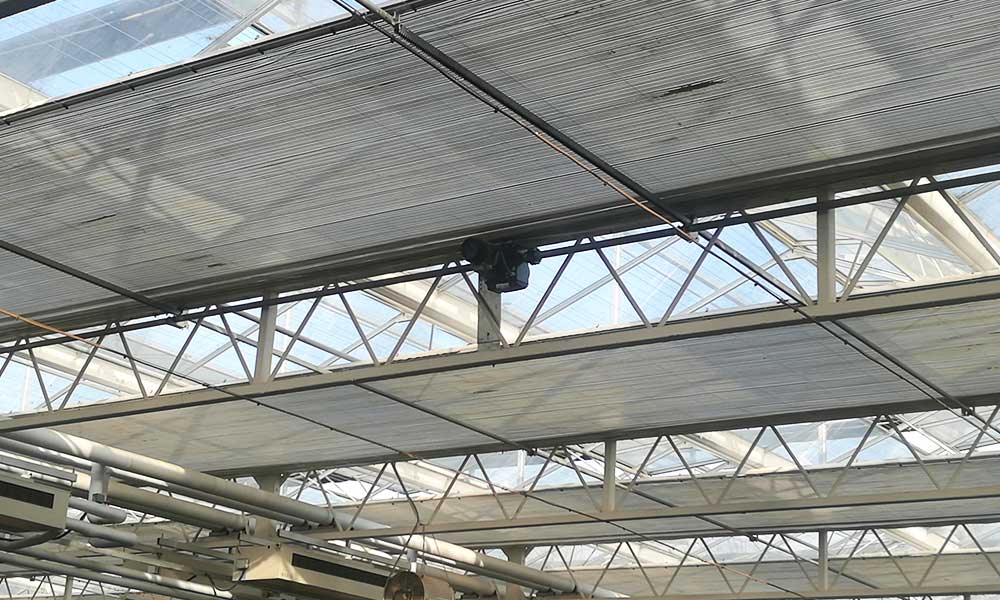
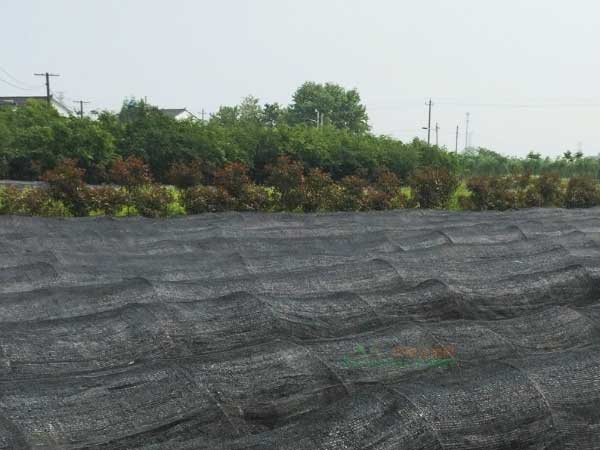
Greenhouse Internal Shading Curtains
2. Cooling Performance
Good shading effectiveness leads to good cooling performance. These materials can provide suitable temperatures inside your greenhouse, promoting the healthy growth of your crops.
3. Material Durability
If the greenhouse covering material is like skin, then the shading material is like clothing or a mask. It is directly exposed to high temperatures, so it needs to be structurally stable and durable. If the shading material is not durable and requires frequent replacement, it will increase the costs and complexity of maintaining the greenhouse.
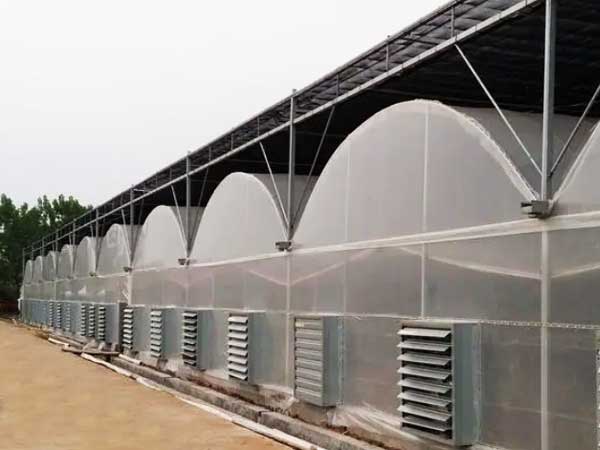

Greenhouse External Shading System
4. Light Transmission and Balance
All plants need photosynthesis, and your greenhouse crops are no exception. Therefore, shading materials need to block sunlight while ensuring adequate light transmission to meet the plants’ photosynthesis needs. Finding the balance between shading and light transmission is key, which requires selecting the appropriate light transmission rate.
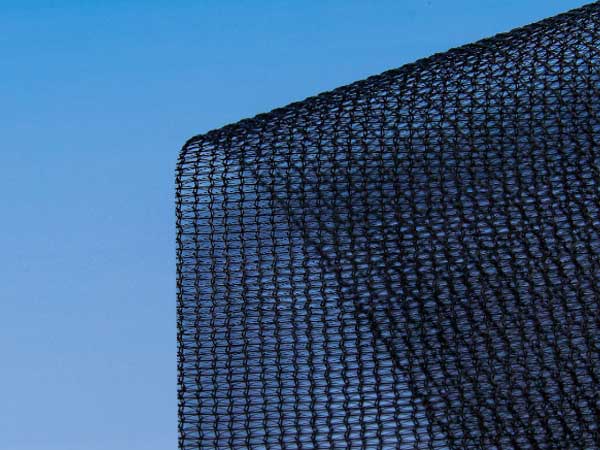

65% Monofilament Shade Net by INSONSHADE
4 Common Types of Shading Materials for Greenhouses
Greenhouse shading materials fall into two categories: fabric used inside the greenhouse or as curtains, commonly known as shade cloth or greenhouse shade screens, and shading agents (or diluted latex paint) applied externally. The most commonly used materials for shade cloth are polypropylene, high-density polyethylene (HDPE), and aluminum.
1. Polypropylene Shade Net
Polypropylene is known for its heat resistance, corrosion resistance, and low density, making it the lightest general-purpose plastic. However, it has poor low-temperature impact resistance and tends to age quickly. Adding ethylene to polypropylene can improve its impact resistance, with higher ethylene content resulting in greater strength.

Polypropylene Shade Net
2. HDPE Shade Net
HDPE is stable and can endure prolonged exposure to high temperatures without degradation. It is also resistant to external impacts, making it durable and less likely to crack or break. High-quality HDPE shade nets often include UV stabilizers to enhance their stability in high temperatures, extending their lifespan. Typically, HDPE shade nets offer a shading rate between 30% and 90%, with some high-density options exceeding 95%.
INSONSHADE HDPE Shade Nets
3. Aluminum Shade Curtains
Aluminum shade curtains are made from polyethylene and woven aluminum foil strips, providing a shading rate between 30% and 100%. Compared to other shade cloths, aluminum shade screens have distinct advantages.
They can reflect a portion of the sunlight, reducing direct sunlight entering the greenhouse and helping to maintain cooler temperatures. In addition, these screens evenly disperse sunlight throughout the greenhouse, preventing hot spots and ensuring that all parts of your crops receive adequate light for photosynthesis.
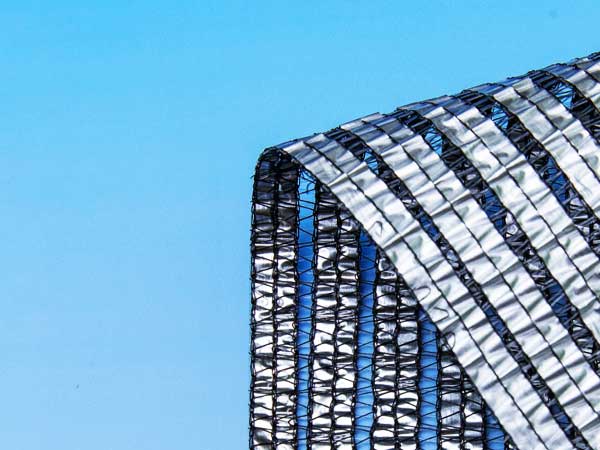

Aluminum Shade Curtain for Commercial Greenhouse by INSONSHADE
These features make aluminum shade screens effective in reducing heat accumulation inside the greenhouse and maintaining optimal temperatures and lighting for healthy plant growth.
4. Shading Agents
Shading agents are the only shading materials applied externally to the greenhouse. According to “The Hobby Greenhouse” by the Ferguson College of Agriculture at Oklahoma State University, shading agents should only be used on glass coverings, as they may damage other materials and be difficult or impossible to remove. Before fall, the shading agent must be washed off the glass to ensure adequate light penetration during the fall and winter, providing your crops with enough light and warmth.
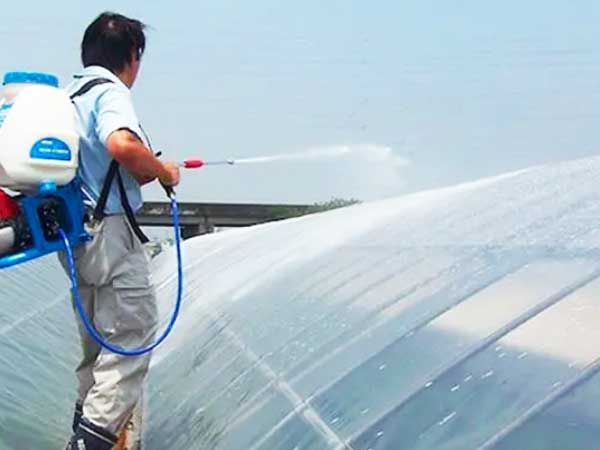

Shading Agents for Poly Greenhouse
How to Choose the Right Greenhouse Shading Material?
Now that you understand the different types of greenhouse shading materials, it’s time to select the one that best suits your crops. To ensure the best choice, consider two main aspects: specific needs and cost. Due to the unique nature of shading agents, we will mainly compare PP, HDPE, and aluminum shade nets.
1. Choosing Based on Specific Needs
This section focuses on the requirements of your greenhouse crops and the scale and purpose of your greenhouse.
- Different Plants’ Light and Temperature Needs: Different plants have unique light and temperature requirements. We have dedicated articles explaining the optimal shading rates for various greenhouse crops.
- Greenhouse Scale and Purpose: The size and purpose of your greenhouse are crucial in selecting shading materials. For large commercial greenhouses, we recommend using HDPE or aluminum shade nets because they typically offer higher durability and better shading effects. Although the initial cost is higher, their long lifespan can save you money in the long run. For small household greenhouses or short-term shading needs, consider the more affordable PP shade net. This type of shade net is cost-effective and suitable for projects with limited budgets.
2. Considering Costs
- Material Cost Comparison: The cost of shading materials varies significantly. PP shade nets are the least expensive because their raw materials and production processes are relatively simple. HDPE shade nets are slightly more costly due to a more complex production process and higher raw material costs. Aluminum shade nets are the most expensive, mainly because of the high price of aluminum foil and the advanced technology required for manufacturing. When choosing, compare costs based on your budget to find the most suitable option.
- Material Quality: When choosing PP and HDPE, avoid the temptation to select solely based on price. Be wary of low-quality shade nets made from recycled materials. Ensure you purchase high-quality products made from new raw materials. Before buying, inquire about the source and quality of the shade net materials to avoid future problems caused by inferior products. Additionally, when purchasing PP shade nets, ask about the proportion of ethylene added, as the impact strength of PP increases with higher ethylene content. When buying HDPE, ask if UV stabilizers are included.
Conclusion
In summary, we have discussed the key factors to consider when choosing shading materials for a greenhouse and highlighted some of the best options for hot climates. Other methods, such as ventilation and air conditioning systems, may also be necessary to optimize the greenhouse environment.
If you would like to learn more or purchase greenhouse shading materials, please contact us. We are committed to providing the highest-quality agro-shading materials, including standard HDPE shade cloth and specialized climate screens for commercial greenhouses, ensuring your greenhouse achieves optimal results.
